Stranded Steel Wire for Cables: Technical Specifications and Selection Guide
Stranded steel wire serves as a critical component in cable manufacturing, primarily designed to enhance mechanical strength and tensile resistance. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of stranded steel wire characteristics, covering specifications, applications, material requirements, and galvanization standards. Aligned with China's National Standard GB/T 20118-2006, it offers professional recommendations for product selection and usage.

1. Specification Categories
1.1 Small-Diameter Stranded Wire
Common configurations:
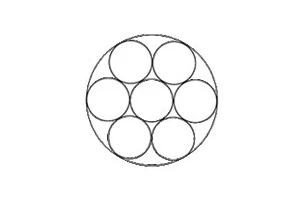
1×7 structure: 0.85mm, 1.0mm, 1.2mm
1×19 structure: 1.0mm, 1.2mm, 1.5mm, 2.0mm
Applications:
Small-diameter cables and fiber optic cables.
Scenarios demanding high mechanical strength and tensile performance.
1.2 Large-Diameter Stranded Wire
Common configurations:
1×7 structure: 2.4mm, 2.7mm, 3.0mm, 3.96mm, 4.8mm
Applications:
Large-scale communication and power transmission projects.
Environments requiring exceptional load-bearing capacity and durability.
1.3 Fiber Optic Cable Reinforcement Wire
Common specifications:
0.45mm, 0.7mm, 0.8mm, 0.9mm, 1.0mm, 1.2mm, 1.4mm, 1.6mm
Most-used sizes:
0.45mm and 1.0mm
Applications:
Core reinforcement for fiber optic cables to improve tensile resistance.
2. Material Requirements
2.1 Phosphated Steel Wire
Features:
Phosphating surface treatment ensures rust resistance and adhesion.
Strict requirements for coating thickness and uniformity.
Applications:
Ideal for fiber optic cables operating in harsh environments.
2.2 Galvanized Steel Wire
Types:
Hot-dip galvanized: Thicker zinc layer for superior corrosion resistance.
Electro-galvanized: Thinner coating suitable for short-term use.
Zinc Coating Standards:
Compliance with GB/T 20118-2006 for zinc content and thickness.
Applications:
Cables and fiber optics requiring enhanced corrosion protection.
3. Galvanization Standards (GB/T 20118-2006)
3.1 Zinc Coating Requirements
Hot-dip galvanized wire:
Thickness: 20–60 μm
Weight: Determined by wire diameter and application.
Electro-galvanized wire:
Thickness: 5–20 μm
Weight: Determined by wire diameter and application.
3.2 Testing Methods
Thickness: Magnetic gauges or microscopy.
Weight: Chemical dissolution or gravimetric analysis.
4. Selection Guidelines
4.1 Small-Diameter Cables
Recommended specifications:
1×7: 0.85mm, 1.0mm, 1.2mm
1×19: 1.0mm, 1.2mm, 1.5mm
Material options:
Phosphated wire: Standard environments.
Galvanized wire: High-corrosion environments.
4.2 Large Communication Projects
Recommended specifications:
1×7: 2.4mm, 2.7mm, 3.0mm, 3.96mm, 4.8mm
Material options:
Hot-dip galvanized wire: Long-term exposure to corrosive conditions.
4.3 Fiber Optic Cables
Recommended specifications:
0.45mm, 1.0mm (most common)
Material options:
Phosphated wire: General-purpose fiber optics.
Galvanized wire: Specialty applications.
5. Usage and Maintenance
Installation: Ensure secure integration with insulation layers and sheaths; avoid mechanical damage.
Inspection: Regularly check for surface wear or corrosion; replace compromised wires promptly.
Environment: Use hot-dip galvanized or anti-corrosion coatings in harsh conditions; phosphated or electro-galvanized wires suffice for dry environments.
Specification Comparison Chart
| Specification | Application Scenario | Material Option | Compliance Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1×7-0.85mm | Small cables | Phosphated/Electro-galvanized | GB/T 20118-2006 |
| 1×7-1.0mm | Small cables/fiber optics | Phosphated/Electro-galvanized | GB/T 20118-2006 |
| 1×7-1.2mm | Small cables | Phosphated/Electro-galvanized | GB/T 20118-2006 |
| 1×19-1.0mm | Small cables | Phosphated/Electro-galvanized | GB/T 20118-2006 |
| 1×19-1.2mm | Small cables | Phosphated/Electro-galvanized | GB/T 20118-2006 |
| 1×19-1.5mm | Small cables | Phosphated/Electro-galvanized | GB/T 20118-2006 |
| 1×19-2.0mm | Small cables | Phosphated/Electro-galvanized | GB/T 20118-2006 |
| 1×7-2.4mm | Large communication projects | Hot-dip galvanized | GB/T 20118-2006 |
| 1×7-2.7mm | Large communication projects | Hot-dip galvanized | GB/T 20118-2006 |
| 1×7-3.0mm | Large communication projects | Hot-dip galvanized | GB/T 20118-2006 |
| 1×7-3.96mm | Large communication projects | Hot-dip galvanized | GB/T 20118-2006 |
| 1×7-4.8mm | Large communication projects | Hot-dip galvanized | GB/T 20118-2006 |
| 0.45mm | Fiber optics | Phosphated/Galvanized | GB/T 20118-2006 |
| 1.0mm | Fiber optics | Phosphated/Galvanized | GB/T 20118-2006 |
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate stranded steel wire for cables requires careful consideration of specifications, materials, and environmental demands. Adherence to GB/T 20118-2006 ensures optimal mechanical performance and longevity. By aligning choices with project-specific needs, users can achieve enhanced safety and reliability in cable systems.